SUMMARY
This is AI generated summarization, which may have errors. For context, always refer to the full article.
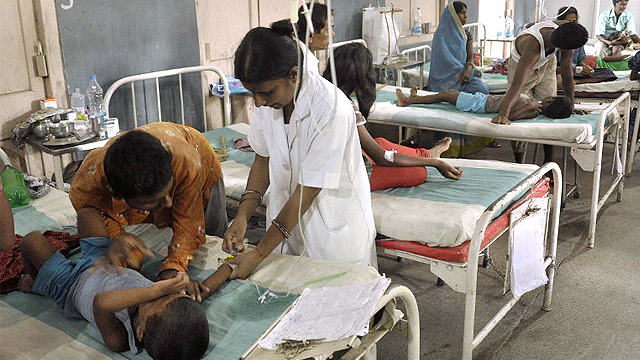
NEW DELHI, India – The fatal poisoning of 23 Indian children has rocked trust in the world’s largest free school meals scheme, but experts say some pupils have no choice but to eat the lunches.
The nationwide scheme feeds some 120 million youngsters every day and is seen as key to persuading parents who are battling poverty to send their children to school rather than condemn them to illiteracy and malnutrition.
But since dozens of pupils fell ill last Tuesday, July 16, at a primary school in the eastern state of Bihar, reports have emerged of other mass hospitalizations and even maggots being found in some meals.
Tens of thousands of children were reported to be refusing to eat their lunches in the immediate aftermath of the tragedy.
While there has been widespread revulsion over the revelations, experts say the scheme is nevertheless a crucial weapon in the war against malnutrition and also serves to undercut caste prejudice.
Forensic tests have shown that the oil used to cook the lunch in Bihar contained a “highly toxic” form of insecticide, underlining fears that monitoring of food quality is inadequate.
The children died after eating lentils, potatoes and rice cooked with oil containing an agricultural insecticide that was five times the strength sold in the market place, according to the tests.
“I can accept accidents can happen anywhere,” activist Dipa Sinha of the Right to Food Campaign told AFP.
“But the scale of this incident and the carelessness, the sheer callousness of the response, the delay in treating the children, is shocking.”
The tragedy may have caused widespread shock but it is hardly an isolated incident.
Twenty children were admitted to hospital Friday, July 19, after they ate lunch at school in the state of Goa, although they were all later released.
Last year more than 130 students needed hospital treatment in the western city of Pune after eating a school lunch, the Times of India reported. A probe revealed that the food was contaminated with E. coli bacteria.
No choice
But Alex George, of ActionAid India’s Child Rights Hub, told AFP poor families had little choice but to allow their children to take part in the scheme.
“For them, this midday meal is often the only wholesome meal they may get in a day.”
A government survey last year found that 42 percent of Indian children under the age of five were underweight.
Several parents who lost children in the Bihar tragedy said they had relied on the school to serve their kids their one square meal of the day.
“We have no food at home and it was only to ensure that my children got at least some food that I sent them to the school,” Sanjudevi Mahatoshe, a mother who lost three children in the tragedy, told AFP.
For all its faults, advocates of the program say the scheme does bring major benefits, not least by erasing social boundaries as children of different castes eat together.
“It has had a huge impact — not just on enrollment, but also on retention rates, Delhi-based economist Reetika Khera told AFP.
“Poorer kids tend to spend more years in school, thanks to the midday meal.”
Tamil Nadu was the first Indian state to adopt a school feeding program in 1982.
Other local governments gradually followed and in 2001, India’s Supreme Court ordered all states to provide free lunches to students in state-run primary schools.
Criticisms
A 2010 government planning commission report on the scheme found the majority of the schools sampled lacked fully functional kitchens, enough utensils and adequate storage space.
Most states also suffered from a shortage of cooks, forcing teachers to buy food and serve meals and in some cases, requiring students to wash utensils.
The commission also criticized local authorities for not doing enough to streamline food supply processes, citing instances “where due to long supply chain, food grain supplied got adulterated and pilfered”.
The report singled out Bihar for its “erratic supply of funds and food grain”, saying that schools rarely received food grains on schedule, “as a result of which a few schools were overstocked resulting in breeding of insects”.
Still, many of the states involved have established effective meal programs, Khera said.
“Some states have shot ahead. Rajasthan provides fresh fruit in addition to the meal twice a week, Orissa provides a boiled egg twice a week,” Khera said.
“Like Bihar, they are poor states but they have the political will and they have made child health a priority.”
While “poor infrastructure and inefficiency are certainly a problem, the lack of monitoring is a huge issue,” said Sinha of the Right to Food Campaign.
“The scheme works, it brings children from the poorest families to school and it ensures that they stay in school. All it needs to function well is a measure of political will,” Sinha said. – Rappler.com
Add a comment
How does this make you feel?
There are no comments yet. Add your comment to start the conversation.