SUMMARY
This is AI generated summarization, which may have errors. For context, always refer to the full article.
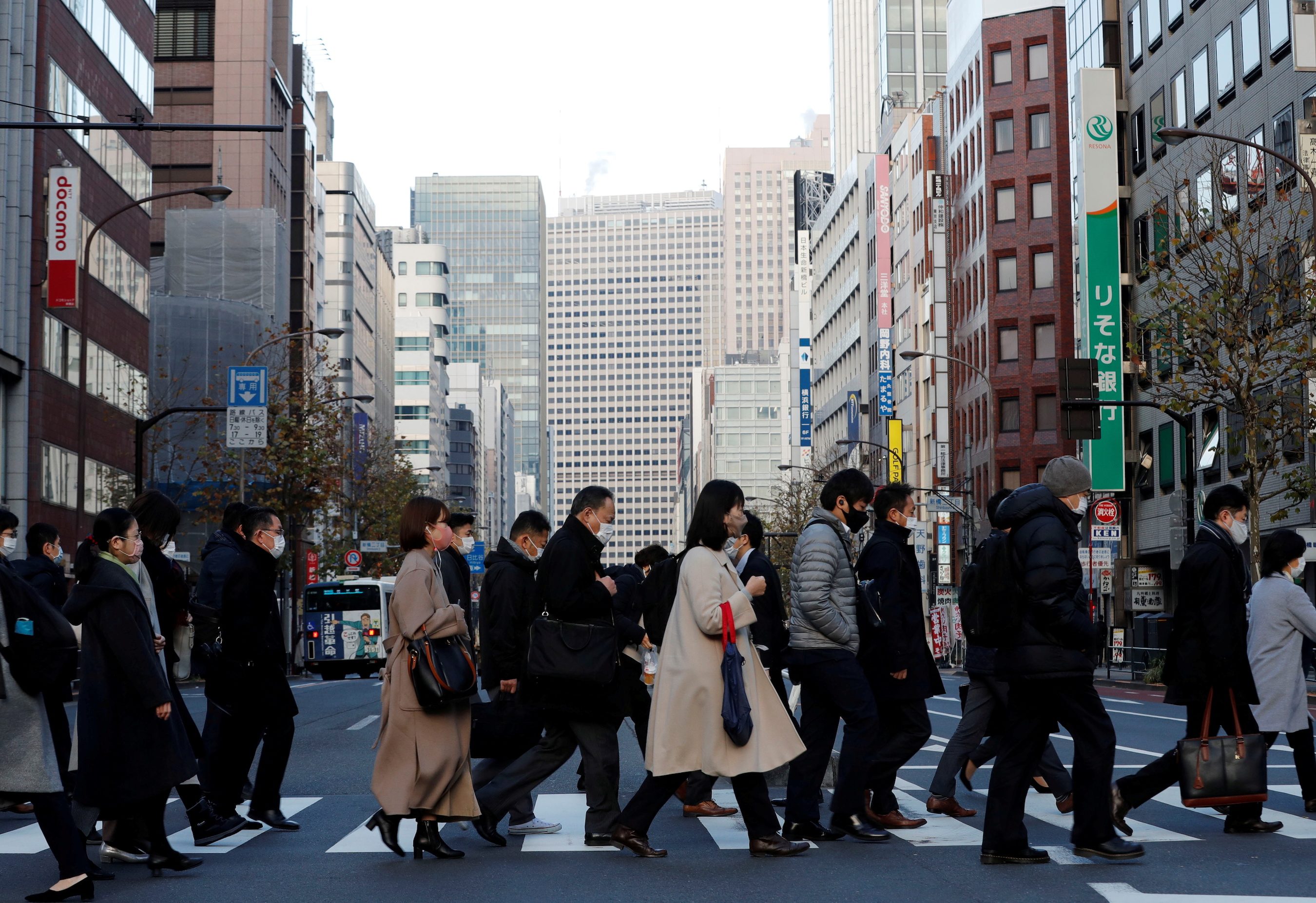

Japan’s economy expanded more than expected in the 4th quarter, extending the recovery from its worst postwar recession thanks to a rebound in overseas demand that boosted exports and capital spending.
But the recovery slowed from the 3rd quarter’s brisk pace and new state of emergency curbs cloud the outlook, underscoring the challenge policymakers face in preventing the spread of COVID-19 without choking off a fragile recovery, especially in the battered consumer sector.
“Conditions are such that Japan will not be able to avoid negative growth in the 1st quarter,” said Takumi Tsunoda, senior economist at Shinkin Central Bank Research.
“There is a high possibility that there will be a repeating cycle of coronavirus infections spreading and being contained this year, which means that consumption is not likely to recover at the expected pace.”
The world’s 3rd largest economy grew an annualized 12.7% in October-December, government data showed on Monday, February 15, exceeding a median market forecast of 9.5%.
It was slower than the revised 22.7% surge in the previous quarter, when the economy got a lift from pent-up demand after a previous state of emergency was lifted in May.
For the full coronavirus-stricken year, Japan’s economy contracted 4.8%, the first annual fall since 2009.
But Japan’s October-December performance was stronger than United States growth of 4% and a 2.8% slump in the eurozone. With two straight quarters of solid growth, Japan’s economy likely recouped 90% of pandemic-induced losses, analysts say.
“Japan’s recovery proceeded at a much faster pace than initially expected,” said Yoshiki Shinke, chief economist at Dai-ichi Life Research Institute.
“There’s still some distance toward a full normalization, but economic activity is recovering toward pre-pandemic levels.”
Japanese shares surged to close at over 30-year highs on rising expectations for a rebound in corporate earnings and economic growth.
Outlook murky
Japan’s stronger-than-expected gross domestic product (GDP) data comes amid signs the pandemic’s hit to other Asian economies toward the end of last year was not as severe as first feared.
Figures released on Monday showed that GDP in Singapore and Thailand shrank less than expected in the fourth quarter.
A global rebound in manufacturing gave Japan’s exports and capital expenditure a much-needed boost on strong shipments to a rapidly recovering Chinese economy.
External demand, or exports minus imports, added 1% to 4th quarter GDP growth thanks to an 11.1% surge in exports buoyed by shipments of electronic parts and autos to China.
Capital expenditure also grew 4.5%, marking the first increase in 3 quarters, as companies proceeded with spending that had been put off last year due to the pandemic.
Private consumption, which makes up more than half of the economy, rose 2.2%, slowing from the 5.1% increase in the previous quarter but exceeding market forecasts for a 1.8% gain.
The outlook, however, remains highly uncertain as Japan lags western countries in rolling out vaccines.
A resurgence in infections forced the government to terminate a controversial travel discount campaign that had supported service spending in October and November.
Analysts expect the economy to contract in the current quarter, as retailers take a hit from renewed state of emergency curbs rolled out in January and set to last until early March.
“If state of emergency measures are lifted in March, Japan’s economy will probably rebound in April-June,” said Yusuke Shimoda, senior economist at Japan Research Institute.
“But we can’t count on a big expansion as it’s likely to take time for vaccine shots to reach the wider population.”
Economy Minister Yasutoshi Nishimura said the economy in the current quarter would unlikely suffer a contraction as large as its worst postwar slump earlier last year.
“I don’t expect the economy will shrink as much as we saw last spring but there are people who are in a severe situation, so we want to support businesses, jobs, and people’s livelihoods.” – Rappler.com
Add a comment
How does this make you feel?


![[Time Trowel] Evolution and the sneakiness of COVID](https://www.rappler.com/tachyon/2024/02/tl-evolution-covid.jpg?resize=257%2C257&crop=455px%2C0px%2C1080px%2C1080px)






There are no comments yet. Add your comment to start the conversation.