SUMMARY
This is AI generated summarization, which may have errors. For context, always refer to the full article.
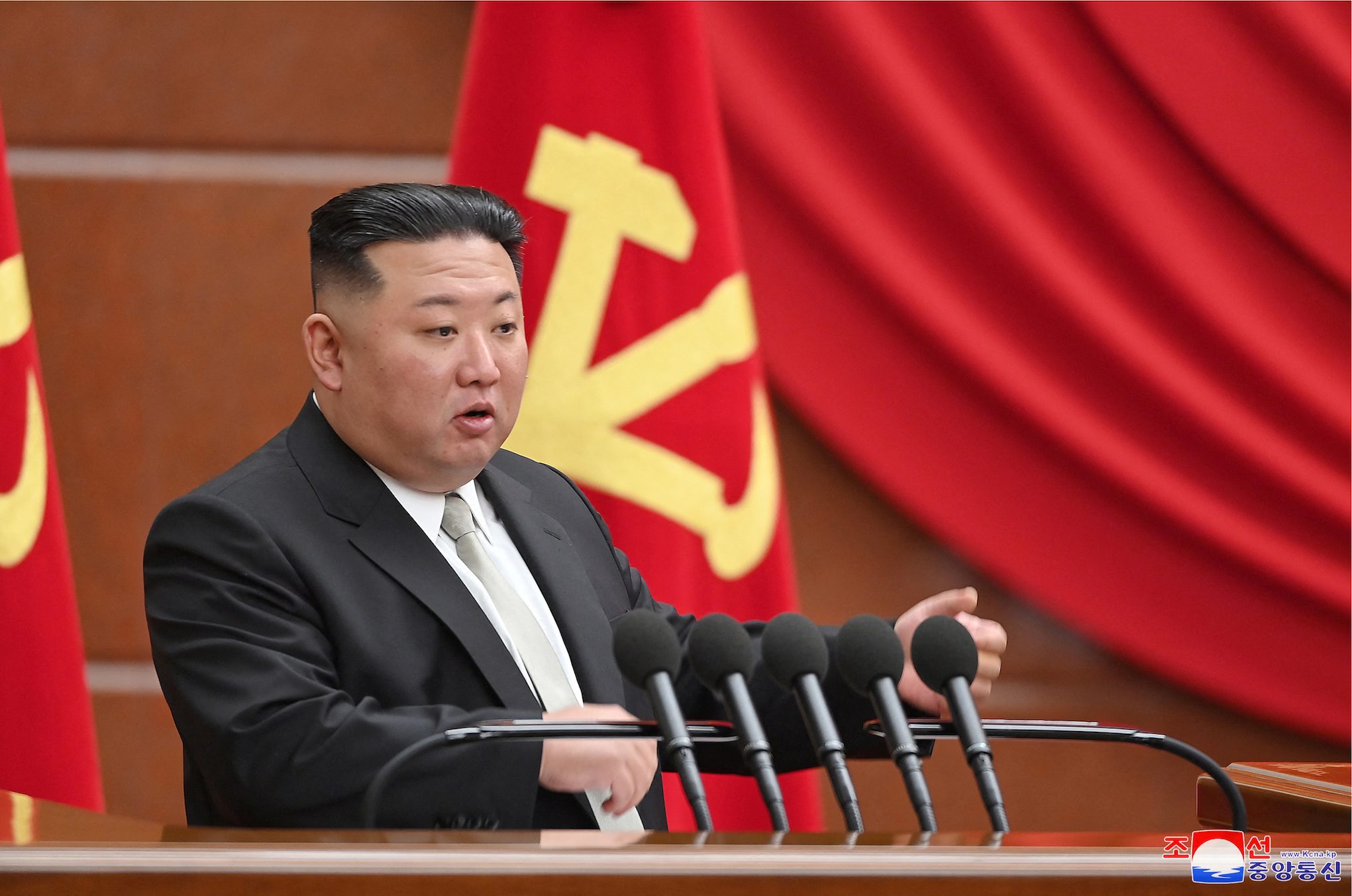

SEOUL, South Korea – North Korea launched a long-range ballistic missile into the sea off Japan’s west coast on Saturday, February 18, after warning of a strong response to upcoming military drills by South Korea and the United States.
Japanese authorities said the missile plunged into waters inside Japan’s exclusive economic zone more than an hour after it was launched, suggesting the weapon was one of Pyongyang’s largest missiles.
Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kisihda said the missile appeared to have been ICBM-class, referring to an intercontinental ballistic missile. He told a briefing Japan strongly condemned the launch, calling it a threat to the international community.
Defense Minister Yasukazu Hamada said the missile appeared to have a range of more than 14,000 kilometers (8,700 miles) – sufficient to reach the US mainland.
Tokyo said there were no immediate reports of damage to ships or aircraft.
In South Korea, which denounced the launch as a “clear breach of UN Security Council resolutions”, the joint chiefs of staff said the missile had flown about 900 kilometers (560 miles) before splashing into the sea.
North Korea’s first missile firing since January 1 came after Pyongyang threatened on Friday an “unprecedentedly persistent, strong” response as South Korea and the United States gear up for annual military exercises as part of efforts to fend off the North’s growing nuclear and missile threats.
Following Saturday’s launch, South Korea’s National Security Council convened a meeting and agreed to increase cooperation on security with Washington and Japan.
The US Indo-Pacific Command said in a statement that US commitments to the defense of Japan and South Korea “remain ironclad.”
“While we have assessed that this event does not pose an immediate threat to US personnel, or territory, or to our allies, we will continue to monitor the situation,” the statement added.
Solid-fuel missile progress?
Nuclear-armed North Korea fired an unprecedented number of missiles last year, including ICBMs that are capable of striking anywhere in the United States, while resuming preparations for its first nuclear test since 2017.
Saturday’s missile was launched from the Sunan area near Pyongyang, South Korea’s military said. Sunan is the site of the Pyongyang International Airport, where North Korea has conducted most of its recent ICBM tests.
North Korea’s ballistic missile and nuclear weapons programs are banned under UN Security Council resolutions, but Pyongyang says its weapons development is necessary to counter “hostile policies” by Washington and its allies.
Allied nuclear drills, called the Deterrence Strategy Committee Tabletop Exercise, are scheduled for Wednesday at the Pentagon and will involve senior defense policymakers from both sides, Seoul’s Defense Ministry said.
The two countries are also planning a range of expanded field exercises, including live fire drills, in the coming weeks and months.
Some 28,500 US troops are stationed in South Korea as a legacy of the 1950-1953 Korean War, which ended in an armistice rather than a full peace treaty, leaving the parties technically at war.
Pyongyang may have created a military unit tasked with operating new ICBMs, in line with its recent restructuring of the military, state media video footage from a Feb. 9 parade suggested.
That parade displayed more ICBMs than ever before, including a possible new solid-fuel weapon, which could help the North deploy its missiles faster in the event of a war.
“North Korean missile firings are often tests of technologies under development, and it will be notable if Pyongyang claims progress with a long-range solid-fuel missile,” said Leif-Eric Easley, a professor of international studies at Ewha University in Seoul. – Rappler.com
Add a comment
How does this make you feel?








There are no comments yet. Add your comment to start the conversation.