SUMMARY
This is AI generated summarization, which may have errors. For context, always refer to the full article.

WASHINGTON, USA – US job growth accelerated in April while wage gains increased solidly, pointing to persistent labor market strength that could compel the Federal Reserve to keep interest rates higher for longer as it fights to bring inflation under control.
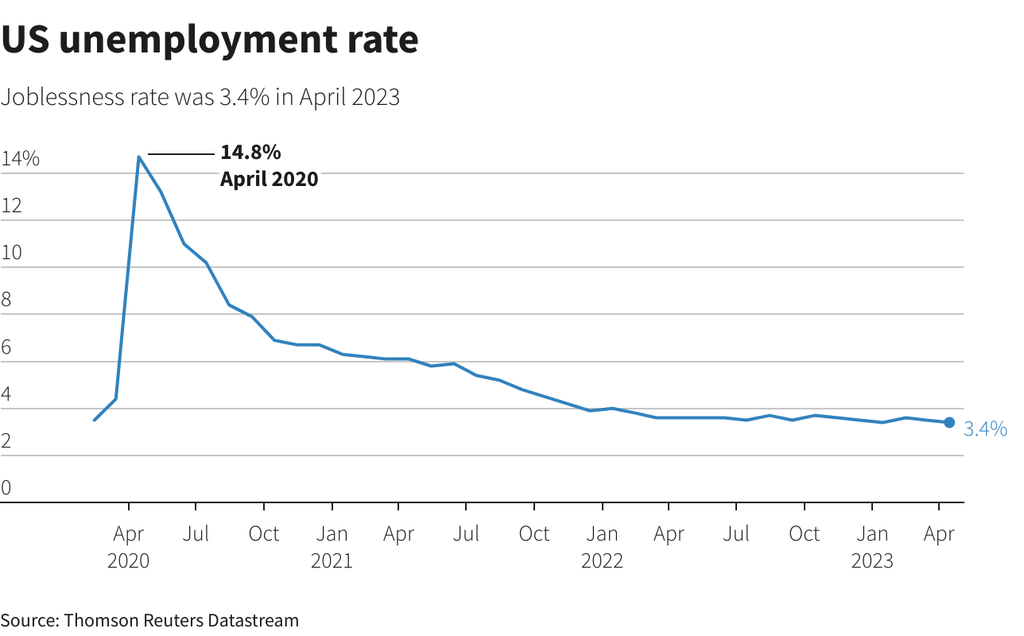
The Department of Labor’s closely watched employment report on Friday, May 5, also showed the unemployment rate falling back to a 53-year low of 3.4%. Though data for February and March were revised sharply lower, the labor market is slowing only marginally. It suggested there was no impact yet on the economy from tighter credit conditions, which together with the Fed’s punitive rate hikes have raised the risk of a recession.
“Interest rates are going to have to remain elevated,” said Sean Snaith, director of the University of Central Florida’s Institute for Economic Forecasting. “This kind of strength in the labor market makes it more difficult for the Fed to continue its reduction in inflation.”
Nonfarm payrolls rose by 253,000 jobs last month, but the economy created 149,000 fewer jobs in February and March than previously reported. Job growth has averaged 290,000 jobs per month over the prior six months. Economists polled by Reuters had forecast payrolls would rise by 180,000.

The economy needs to create 70,000 to 100,000 jobs each month to keep up with growth in the working-age population. The share of private industries adding jobs rose to 57.4% from 57%.
The larger-than-expected increase in payrolls could be hinting at some spring revival in the economy after activity slowed in February and March.
Data this week showed manufacturing pulling off a three-year low and growth in the services sector picking up a bit. Motor vehicle sales also accelerated last month.

President Joe Biden seized on the employment report to urge Congress to raise the federal government’s borrowing cap amid projections it may run out of money in June, a development that could cause great harm to the economy.
“The last thing this country needs, after all we have been through, is a manufactured crisis,” Biden said ahead of a meeting on US investment. “It’s a manufactured crisis driven by MAGA Republicans in Congress.” MAGA is the acronym for the “Make America Great Again” slogan of former president Donald Trump.
The US central bank raised its benchmark overnight interest rate by another 25 basis points to the 5%-5.25% range on Wednesday, May 3, and signaled it may pause its fastest monetary policy tightening campaign since the 1980s, though it kept a hawkish bias. The Fed has hiked its policy rate by 500 basis points since March 2022.
The service-providing sector accounted for most of the job gains in April, with professional and business services adding 43,000 positions. But temporary help services employment, seen as a harbinger for future hiring, dropped by just over 23,000 positions and is down by 174,000 since its peak in March 2022.
Healthcare payrolls increased by 40,000. Employment in the leisure and hospitality industry rose by 31,000 jobs, mostly concentrated at restaurants and bars. Hiring in the sector, which has been the main job growth driver, is slowing. Employment in the industry remains 402,000 jobs below its pre-pandemic level.

Financial activities payrolls rose by 23,000, as did the government jobs category. Government employment remains 301,000 positions below its pre-pandemic level. Manufacturing, retail, and construction payrolls rebounded after declining in March.
The report poured cold water on financial market expectations that the Fed would start cutting interest rates this year. Consumer price index data for April, due to be released next Wednesday, May 10, will offer more clues on the near-term path of monetary policy.
Stocks on Wall Street were trading higher. The dollar fell against a basket of currencies. US Treasury yields rose.

Solid wage gains
Some economists said worker hoarding by businesses after difficulties finding labor in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic was contributing to strong job growth, which most expected to persist at least until the fourth quarter.
Average hourly earnings gained 0.5% last month after advancing 0.3% in March. Wages increased 4.4% on a year-on-year basis in April after climbing 4.3% in March, coming close to alignment with other measures such as the Employment Cost Index and the Atlanta Fed’s wage tracker. Wage growth is too strong to be consistent with the Fed’s 2% inflation target.

While the workweek was unchanged at 34.4 hours, total hours worked rose 0.2%. This generated a 0.7% gain in payrolls.
The pickup in business output early in the second quarter and the rise in hours worked bodes well for a bounce-back in productivity, which surged right after the pandemic in 2021, but has declined on a year-over-year basis since then for five straight quarters, the longest such stretch since the government started tracking the series in 1948.
“Prospects for a rebound in productivity in the second quarter look good,” said Brian Bethune, an economics professor at Boston College. “That will restrain unit labor costs, and all other costs should see the first outright decline in many years. The prospects for gradual disinflation in the second and third quarters still look good.”
Details of the household survey from which the unemployment rate is calculated were upbeat. Household employment increased, while the labor force fell modestly.
That caused the jobless rate to dip to 3.4%, matching the lowest level since 1969, from 3.5% in March. The unemployment rate for Blacks hit a fresh record low of 4.7%.
The labor force participation rate, or the proportion of working-age Americans who have a job or are looking for one, was unchanged at 62.6%. But the share of those aged 25 to 54 rose to a 15-year high of 83.3%.
The prime-age employment-to-population ratio, viewed as a measure of an economy’s ability to create employment, rose to 80.8%, the highest level since May 2001.
“Recession has not yet begun,” said Steven Blitz, chief US economist at TS Lombard in New York. – Rappler.com
Add a comment
How does this make you feel?

![[OPINION] A rebellion long overdue](https://www.rappler.com/tachyon/2024/06/mass-uprising-matrix-june-4-2024.jpg?resize=257%2C257&crop_strategy=attention)













There are no comments yet. Add your comment to start the conversation.